Risk management report
The following section discusses the various aspects of enterprise-wide risk management. Readers are cautioned that the risk related information outlined here is not exhaustive and is for information purpose only. The discussion may contain statements, which may be forward-looking in nature. Our business model is subject to uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those reflected in the forward-looking statements. Readers are requested to exercise their own judgment in assessing the risks associated with the Company and to refer to the discussions of risks in the Company's previous Annual Reports and the filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, USA.
A. Overview
The Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) at Infosys encompasses practices relating to identification, assessment, monitoring and mitigation of various risks to our business. ERM at Infosys seeks to minimize adverse impact on our business objectives and enhance stakeholder value. Further, our risk management practices seek to sustain and enhance long-term competitive advantage of the Company. Risk management is integral to our business model, described as ‘Predictable, Sustainable, Profitable and De-risked’ (PSPD) model. Our core values and ethics provide the platform for our risk management practices.
B. Our Risk Management Framework
Our risk management framework encompasses the following key components.
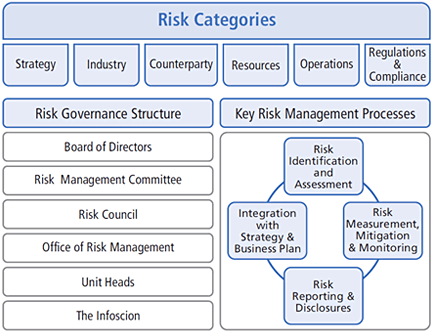
1. Risk management structure
Our risk management occurs across the enterprise at various levels. These levels also form the various lines of defense in our risk management.
The key roles and responsibilities regarding risk management in the Company are as follows :
Level |
Key roles and responsibilities |
| Board of Directors (Board) |
|
| Risk Council (RC) |
|
| Office of Risk Management (ORM) |
|
| Unit Heads |
|
| The Infoscion |
|
(1) As of April 13, 2010
2. Risk categories
The following broad categories of risks have been considered in our risk management framework :
- Strategy : Risks emanating out of the choices we make on markets, resources and delivery model that can potentially impact our
long-term competitive advantage. - Industry : Risks relating to inherent characteristics of our industry including competitive structure, technological landscape, extent of linkage to economic environment and regulatory structure.
- Counterparty : Risks arising from our association with entities for conducting business. These include clients, vendors, alliance partners and their respective industries.
- Resources : Risks arising from inappropriate sourcing or sub-optimal utilization of key organizational resources such as talent, capital and infrastructure.
- Operations : Risks inherent to business operations including those relating to client acquisition, service delivery to clients, business support activities, information security, physical security and business activity disruptions.
- Regulations and compliance : Risks due to inadequate compliance to regulations, contractual obligations and intellectual property violations leading to litigation and loss of reputation.
3. Key risk management practices
The key risk management practices include those relating to risk assessment, measurement, mitigation, monitoring, reporting and integration with strategy and business planning.
- Risk identification and assessment : Periodic assessment to identify significant risks for the Company and prioritizing the risks for action. Mechanisms for identification and prioritization of risks include risk survey, business risk environment scanning and focused discussions in RC and RMC. Risk survey of executives across units, functions and subsidiaries is conducted before the annual strategy exercise. Risk register and internal audit findings also provide pointers for risk identification.
- Risk measurement, mitigation and monitoring : For top risks,
dashboards are created that track external and internal indicators relevant for risks, so as to indicate the risk level. The trend line assessment of top risks, analysis of exposure and potential impact are carried out. Mitigation plans are finalized, owners are identified and progress of mitigation actions are monitored and reviewed. - Risk Reporting : Top risks report outlining the risk level, trend line, exposure, potential impact and status of mitigation actions is discussed in RC and RMC on a periodic basis. In addition, risk update is provided to the Board. Entity level risks such as project risks, account level risks are reported to and discussed at appropriate levels of the organization.
- Integration with strategy and business planning : Identified risks are used as one of the key inputs for the development of strategy and business plan.
Key components of Infosys Risk Management Framework
C. Overview of risk environment and key risk management activities of the year
Business risk environment was challenging for most part of the year, primarily driven by the prolonged impact of global economic slowdown on our clients and the resultant impact on our business. Financial position of several key clients who were impacted by the global economic slowdown, gradually improved during the year. Regulatory environment relating to immigration / visa and taxation required close monitoring and assessment. Global currencies from which we derive our revenues showed high volatility. Physical security environment in India called for increased vigilance measures.
Our continued emphasis on credit risk management through periodic credit quality assessments and focused collection mechanisms resulted in further improvement of credit risk indicators. Our active management of currency risks minimized the impact in a volatile currency market. We further strengthened operational risk mitigation mechanisms in areas including physical security, service delivery, information security and contracts management. Our periodic assessment and monitoring of business risk and regulatory environment resulted in deployment of appropriate mitigation measures.
We carried out various risk management activities described as follows, to monitor and mitigate risks :
1. Top risk identification, tracking and review
- Annual risk survey across functions and subsidiaries to get inputs on key risks and prioritization. Subsequent discussions in RC and RMC for finalization of top risks
- Review of top risks in RC and RMC covering risk level, trend line, exposure, potential impact and progress of key mitigation actions
- Review discussions on key items from risk register by RC and RMC.
2. Risk assessments and review
- Periodic assessment of business risk environment including top clients analysis, counterparty exposures and sovereign risk
- Risk assessment of regulatory environment especially those relating to immigration / visa and taxation
- Assessment and review of financial risks such as currency risk, credit risk and liquidity
- Review of risk management practices relating to information security, physical security and service delivery
- Review of rollout of account risk management framework in business units
- Review of progress of ERM implementation in subsidiaries.