Digital Workplace Services
Autonomous Compliance Officer using Agentic AI
This whitepaper explores the ‘Autonomous Compliance Officer’, agentic AI-driven approach, which can be designed to automate and streamline regulatory compliance, via leveraging Generative AI abilities. This system should provide real-time monitoring, automated reporting, reducing operational costs and mitigating regulatory risks.
Insights
- It can automate real-time regulatory monitoring and reporting, significantly reducing manual effort and costs.
- It can use adaptive algorithms to dynamically adjust to evolving regulations and learn from past data.
- It can provide a transparent, auditable compliance trail, enhancing regulatory trust.
- It can signal a shift towards increased automation in financial governance and future regulatory frameworks.
Introduction
This whitepaper introduces a transformative framework for regulatory compliance in multinational banking, leveraging Agentic AI and Modular Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). The proposed 'Autonomous Compliance Officer' system automates regulatory monitoring, reporting, and analysis across jurisdictions, offering real-time insights and adaptive learning capabilities. Key benefits include a projected 50–60% reduction in compliance costs and a 60–70% improvement in reporting accuracy. Architecture supports scalable document ingestion, semantic enrichment, and intelligent orchestration, enabling proactive risk management and ethical governance. This solution empowers financial institutions to navigate complex regulatory landscapes with greater efficiency, transparency, and strategic agility.
Challenges for Multi Nation Banks on navigating regulatory guidelines.
Multinational banks navigate a complex web of regulatory authorities across diverse nations and economic blocks. They are subject to national regulators in each operating country, such as the Federal Reserve and OCC in the US, the ECB’s ESMA (European Securities and Markets Authority) along with each European national competent authorities, ASPRA ( Australian Prudential Regulation Authority Prudential Standard) , MAS ( Monetary Authority of Singapore ) , China’s NFRA ( National Financial Regulatory Administration) and in the case of India , Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in India and many more . Each of these bodies sets specific rules on capital, consumer protection, and operational resilience, requiring banks to tailor their compliance programs accordingly. And with the emerging areas like Open Banking, the rise of mobile banking, crypto money presents a similarly diverse landscape with varying levels of regulatory complexity. And in ever evolving regulatory framework, demands adherence to increasingly stringent compliance measures, including those related to corporate governance and risk control.
Beyond national authorities, multinational banks must also comply with regulations from economic blocks and international bodies, Ex: In Europe, the Single Supervisory Mechanism (SSM) adds a layer of oversight for Eurozone banks, while globally, the Financial Stability Board (FSB) sets standards influencing national rules. Compliance with these international norms, such as the Basel Accords, often requires consistent global policies despite local variations. The increasing focus on cross-border issues like AML/CTF (Combating the Financing of Terrorism), as emphasized by the FATF, and international sanctions further complicates matters, demanding robust global compliance programs.
Not following these will lead to heavy penalties, as illustrated via below snippets of new articles on large multi nation banks:
Danske Bank (Estonian Branch, 2022): |
NatWest (UK, 2021): |
Deutsche Bank (Germany, 2023): |
Goldman Sachs (2020): |
The intricate interplay of national, regional, and international regulations demands that multinational banks maintain sophisticated and adaptive compliance strategies. They require robust internal controls, advanced reporting mechanisms, and a thorough understanding of the specific requirements and enforcement practices in each jurisdiction. The dynamic nature of financial regulations, coupled with the emergence of new technologies and cross-border risks, means that a proactive and comprehensive approach to compliance is essential for multinational banks to operate safely and effectively in the global financial system, avoiding significant penalties and reputational damage.
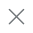
First Steps with Generative AI
We found that in the financial market domain we face significant challenges with the manual analysis of extensive regulatory documents, which are typically 200-300 pages long. This process is not only time-consuming but also prone to errors, increasing the risk of non-compliance and potential penalties. Identifying changes and understanding their impact on new versions of these documents is particularly arduous, leading to delays in compliance and a higher likelihood of missed changes.
Hence to address these issues, we have developed a GenAI-based solution designed to expedite the understanding of regulatory documents.
This solution offers three key capabilities: a Q&A feature that allows users to ask questions and receive precise answers directly from the document, a document summarizer that provides summaries over pages or sections as needed, and a document comparison tool that identifies changes between different releases of a regulation document. These features can be used independently or in combination for comprehensive and accelerated regulatory analysis.
The platform enhances efficiency by saving time and effort, improves accuracy as demonstrated by promising results, and offers better user experience with an improved UI that simplifies complex tasks. Additionally, the solution is scalable, capable of handling various regulatory documents and updates, and shows potential for significant return on investment and cost savings, even at the proof-of-concept stage.
Now, this can be enhanced further by applying the Agentic AI and Modular RAG to provide a generic autonomous platform to analyze regulatory across multiple regions which is shared below.
Why Agentic AI is crucial in Finance Space?
Agentic AI in the financial space represents a paradigm shift, moving beyond passive data analysis to proactive, autonomous decision-making. These AI agents, equipped with planning, reasoning, and learning capabilities, can navigate complex regulatory landscapes, automate compliance procedures, and even detect fraudulent activities in real-time. By acting as intelligent, self-directed entities, they promise to streamline operations, mitigate risks, and enhance efficiency across various financial services.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: Agentic AI can automate compliance monitoring and reporting, reducing the risk of errors and penalties. It can adapt to evolving regulations, ensuring continuous compliance.
- Improved Risk Management: By proactively identifying and assessing risks, agentic AI can help financial institutions mitigate potential losses and enhance their resilience.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Automation of complex workflows can significantly reduce operational costs and free up human resources for more strategic tasks.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Agentic AI can provide insights and recommendations based on data analysis, enabling financial professionals to make more informed decisions.
- Scalability: Agentic AI systems can easily scale to handle large volumes of data and transactions, making them ideal for large financial institutions.
- Reduced human error: Automation significantly lowers the risk of mistakes made by humans, especially when processing large amounts of data.
Our Approach with Modular RAG and Agentic AI
The complexity of handling compliance across multiple nations with numerous documents is where Modular RAG and Agentic AI shine, offering significant advantages over simpler approaches.
Here's a breakdown of why they're the best approach:
1. Scalability and Manageability of Diverse Data:
- Modular RAG's Strength:
- Separation of Concerns: Each nation's or region's compliance documents can be stored in separate modules. This allows for:
- Targeted Updates: When a specific nation's regulations change, only that module needs updating, minimizing disruption.
- Efficient Retrieval: The agent can quickly identify the relevant module based on the user's query (e.g., "GDPR implications for data transfer to Japan").
- Reduced Noise: Prevents irrelevant documents from different nations from polluting the context, leading to more accurate responses.
- Vector Database Organization: The vector database can be structured to reflect the modularity, enabling fast and precise retrieval.
- Separation of Concerns: Each nation's or region's compliance documents can be stored in separate modules. This allows for:
- Agentic AI's Strength:
- Orchestration: The agent can manage the complexity of switching between modules and integrating information from different sources.
- Task Decomposition: It can break down complex, multi-national compliance queries into smaller, manageable steps, such as:
- "Identify the relevant regulations for each nation involved."
- "Retrieve the relevant documents from each module."
- "Compare and contrast the requirements."
- "Generate a consolidated report."
2. Handling Legal Nuances and Language Variations:
- Modular RAG's Strength:
- Language-Specific Embeddings: You can use embedding models fine-tuned for specific languages to improve retrieval accuracy.
- Localized Knowledge Bases: Each module can be tailored to the specific legal language and terminology of the nation.
- Agentic AI's Strength:
- Reasoning and Interpretation: The agent can reason about the subtle differences in legal language and interpretations across nations.
- Contextual Understanding: It can maintain context across multiple interactions, even when dealing with different legal frameworks.
- Translation and Summarization: Agents can be equipped with tools to translate documents or summarize key differences between regulations.
3. Automation and Efficiency:
- Modular RAG's Strength:
- Automated Updates: New regulations can be automatically ingested and indexed into the relevant modules.
- Faster Retrieval: Vector search enables rapid retrieval of relevant information, even from large knowledge bases.
- Agentic AI's Strength:
- Automated Compliance Checks: The agent can automate routine compliance checks across multiple nations.
- Proactive Compliance Monitoring: It can monitor changes in regulations and alert relevant stakeholders.
- Report Generation: The agent can automatically generate compliance reports for different jurisdictions.
4. Adaptability and Extensibility:
- Modular RAG's Strength:
- Easy Expansion: New modules can be added as new nations or regulations are introduced.
- Flexible Architecture: The system can be adapted to different compliance domains and data sources.
- Agentic AI's Strength:
- Tool Integration: The agent can be integrated with new tools and APIs as needed.
- Continuous Improvement: The agent can learn from past interactions and improve its performance over time.
In essence:
- Modular RAG provides the structured and scalable knowledge base necessary to manage diverse, multi-national compliance data.
- Agentic AI provides the intelligence and orchestration needed to navigate the complexities of multiple legal frameworks and generate actionable insights.
This combination creates a powerful and adaptable solution that can handle the challenges of global compliance in a way that simpler approaches cannot.
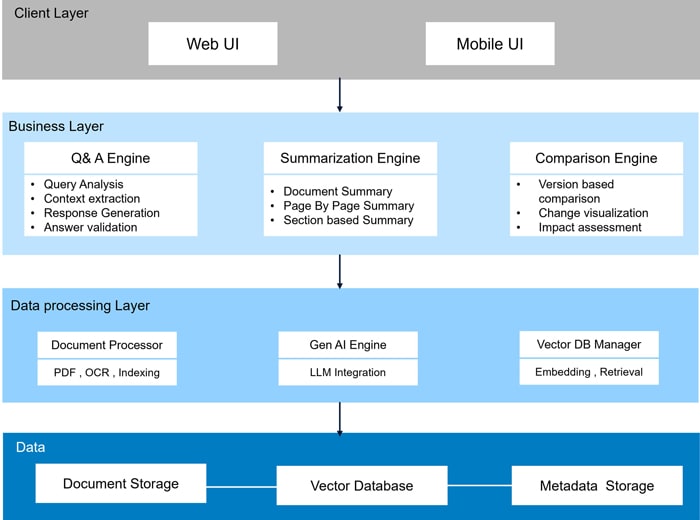
System Architecture
The system employs a Modular Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework integrated with Agentic AI to deliver precise, context-aware compliance information. It encompasses document ingestion, intelligent categorization, efficient retrieval via vector databases, and coherent response generation, all within a structured and scalable knowledge architecture.
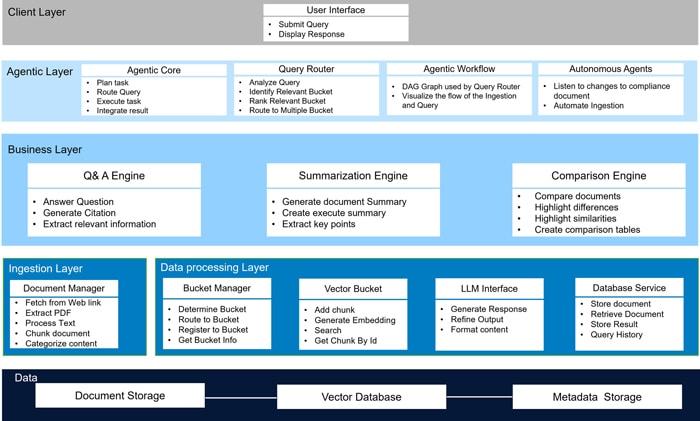
Key Components and their Functions:
- User Interface: Provides the primary point of interaction for users to submit compliance queries (submit Query ()) and receive system responses (display Response ()).
- DocumentManager: Responsible for the intake and preprocessing of compliance documentation, including web retrieval (fetchFromWeblink(url)), PDF extraction (extractPDF(file)), text normalization (processText(content)), document segmentation (chunkDocument(text)), and content categorization (categorizeContent(chunk)).
- BucketManager: Manages the organization of document segments into logical vector databases ("buckets"). Functions include bucket assignment (determine Bucket(content)), routing (routeToBucket (chunk, bucketId)), new bucket registration (registerNewBucket(criteria)), and information retrieval (getBucketInfo ()).
- VectorBucket: Stores document segments as vector embeddings to facilitate efficient semantic retrieval. Attributes include a unique identifier (bucketId), descriptive metadata (description), chunk addition (addChunk(chunk)), embedding generation (generateEmbedding(text)), semantic search (search(query)), and specific chunk retrieval (getChunkById)).
- QueryRouter: Analyzes user queries to determine the most relevant VectorBucket(s) for search. Capabilities include query parsing (analyzeQuery(query)), relevant bucket identification (leveraging the LLMInterface via identifyRelevantBuckets(query)), relevance ranking (rankBucketRelevance (query, buckets)), and query distribution (routeToMultipleBuckets(query)).
- AgentCore: Serves as the central orchestration layer, managing information flow and task execution. Functions include task decomposition (planTask(query)), task routing (routeQuery(task)), task execution and context management (executeTask (task, context)), and result aggregation (integrateResults(results)).
- Autonomous Agents: Serves as the Automated ingestion layer, managing document Ingestion from multiple Regulatory web links.
- SummarizationEngine: Generates concise summaries of retrieved documents (generateSummary(document)), including executive overviews (createExecutiveSummary()) and key point extraction (extractKeyPoints()).
- QAEngine: Provides direct answers to specific questions based on retrieved content (answerQuestion(question, context)), identifying pertinent passages (extractRelevantPassages(question)) and generating citations (generateCitations()).
- ComparisonEngine: Facilitates the comparative analysis of multiple documents (compareDocuments(doc1, doc2)), highlighting similarities (identifySimilarities()) and differences (highlightDifferences()), and generating comparative tables (createComparisonTable()).
- LLMInterface: Provides an abstraction layer for interacting with Large Language Models, enabling text generation (generateResponse(prompt, context)), output refinement (refineOutput(draft)), and content formatting (formatContent(response)).
- DatabaseService: Persists and retrieves documents and processing results, supporting document storage (storeDocument(doc)), retrieval (retrieveDocument(id)), result storage (storeResults(result)), and query history(queryHistory()).
Workflow:
- A user submits a compliance query via the User Interface.
- The AgentCore receives the query, formulates a task plan, and directs it to the QueryRouter.
- The QueryRouter analyzes the query and identifies the semantically relevant VectorBucket(s).
- The QueryRouter dispatches the query to the selected buckets, which perform vector searches to retrieve pertinent document segments.
- The AgentCore delegates subsequent processing tasks (e.g., summarization, question answering, comparison) to the appropriate engine(s) based on the query's nature.
- The designated engines utilize the LLMInterface to generate synthesized outputs.
- The AgentCore aggregates the outputs from the various engines into a cohesive response.
- The User Interface presents the final response to the user.
- The DatabaseService logs the complete interaction for auditability and future reference.
This architecture is designed to provide a robust, adaptable, and scalable solution for managing complex compliance inquiries across diverse document sources.
Potential Use Cases of this Solution Approach
The integration of Agentic AI into compliance management heralds a new era of efficiency and precision. By leveraging autonomous agents, organizations can significantly streamline their compliance processes, mitigate risks, and foster a culture of adherence. Here's a detailed look at the core functionalities:
1. Answering Compliance Queries: Instant and Contextual Expertise
- Functionality:
- Users can pose natural language questions about complex regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOX) or internal policies.
- The agent accesses and processes vast regulatory databases, internal documents, and real-time updates to provide accurate and contextually relevant answers.
- It can break down intricate legal jargon into easily understandable explanations, tailored to the user's role and understanding.
- Benefits:
- Reduces reliance on human experts for routine inquiries.
- Provides immediate access to compliance information, fostering proactive compliance.
- Enhances employees’ understanding of regulatory requirements.
2. Generating Compliance Reports: Automated and Data-Driven Insights
- Functionality:
- The agent automatically extracts and analyzes compliance data from various sources (e.g., databases, logs, transaction records).
- It generates comprehensive reports, including risk assessments, compliance status summaries, and audit trails.
- It can customize reports based on specific requirements and regulatory frameworks.
- Benefits:
- Saves significant time and resources compared to manual report generation.
- Provides accurate and consistent reporting, minimizing human error.
- Enables data-driven decision-making for compliance management.
3. Conducting Compliance Audits: Proactive Risk Identification
- Functionality:
- The agent continuously monitors data for anomalies and potential compliance violations.
- It applies pre-defined rules and AI-powered pattern recognition to identify high-risk areas.
- It can generate detailed audit reports, highlight potential issues and recommend corrective actions.
- Benefits:
- Enables proactive risk mitigation by identifying potential violations early.
- Reduces the scope and cost of manual audits.
- Provides a more comprehensive and objective assessment of compliance.
4. Providing Compliance Training: Personalized and Adaptive Learning
- Functionality:
- The agent creates personalized training modules based on employee roles and compliance needs.
- It uses interactive simulations and quizzes to enhance learning engagement.
- It tracks employee progress and provides feedback, ensuring effective knowledge transfer.
- Benefits:
- Improves employee compliance awareness and knowledge.
- Reduces the risk of compliance violations due to inadequate training.
- Provides cost-effective and scalable training solutions.
5. Automated Policy Updates: Real-Time Regulatory Adaptation
- Functionality:
- The agent continuously monitors regulatory databases and legal publications for updates.
- Upon detecting new regulations, it automatically updates its knowledge base and relevant internal policies.
- It generates notifications and alerts to inform stakeholders about policy changes and required actions.
- Benefits:
- Ensures that compliance policies remain up to date with evolving regulations.
- Reduces the risk of non-compliance due to outdated policies.
- Saves time and effort associated with manual policy updates.
6. Comparing Policies: Cross-Regional Harmonization
- Functionality:
- The agent can compare policy documents across different regions and jurisdictions.
- It can highlight discrepancies, similarities, and potential conflicts between policies.
- It can provide insights into regional variations and best practices.
- Benefits:
- Facilitates policy harmonization and standardization across global operations.
- Reduces the risk of regulatory conflicts and inconsistencies.
- Improves understanding of regional compliance requirements.
7. Common Handling: Global Policy Understanding and Efficiency
- Functionality:
- The agent analyzes policies from various nations to identify commonalities and best practices.
- It promotes a unified approach to compliance management, reducing redundant efforts.
- It develops standardized procedures for handling common compliance issues.
- Benefits:
- Enhances operational efficiency by streamlining compliance processes.
- Reduces workload by identifying and implementing common policy handling.
- Promotes consistency and uniformity in compliance practices across regions.
8. Providing Insights on Regulatory Misinterpretations and Irregularities:
- Functionality:
- The agent can analyze cases of regulatory misinterpretation and irregularities from around the world.
- It can provide insights into how different jurisdictions handle similar situations.
- It can offer recommendations on best practices for addressing and preventing such issues.
- Benefits:
- Provides a global perspective on regulatory challenges.
- Enhances the organization's ability to navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
- Reduces the risk of costly penalties and reputational damage.
Regulatory Alignment
The Autonomous Compliance Officer system has been designed to align with major global regulatory frameworks, ensuring comprehensive and up-to-date compliance. It supports standards such as Basel III for capital adequacy and risk management, GDPR for data privacy and consent, FATF recommendations for AML/CTF monitoring, and sector-specific regulations like SOX and HIPAA. By integrating real-time updates and jurisdiction-specific modules, the platform enables financial institutions to maintain continuous compliance across diverse regulatory landscapes. This alignment not only reduces the risk of non-compliance but also enhances transparency and trust with regulators and stakeholders.
Risk and Limitation Analysis
Despite its transformative potential, the Autonomous Compliance Officer system presents several risks and limitations. AI models may experience model drift if not regularly updated with current regulatory data, leading to outdated compliance decisions. Jurisdictional conflicts can arise due to varying interpretations of regulations across countries, potentially causing inconsistencies. Over-reliance on automation may reduce human oversight, increasing the risk of undetected anomalies. Handling sensitive compliance also raises data privacy concerns, necessitating robust security measures. Scalability across diverse regulatory environments may require significant customization. Mitigation strategies will include regular audits, human-in-the-loop validation, and continuous model updates.
Conclusion
Hence In essence, an Autonomous Compliance Officer powered by Agentic AI revolutionizes regulatory management by automating tasks, providing real-time insights, and ensuring proactive compliance.
This technology empowers organizations to navigate complex regulatory landscapes with greater efficiency and accuracy, ultimately mitigating risks and fostering a culture of ethical business practices.
References
Throughout the preparation of this whitepaper, information and insights were from the below weblink
- AI in Financial Services
- https://www.esma.europa.eu/
- https://www.federalreserve.gov/supervisionreg/topics/reporting.htm
- https://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/bs_viewpublicationreport.aspx
- https://www.justice.gov/archives/opa/pr/danske-bank-pleads-guilty-fraud-us-banks-multi-billion-dollar-scheme-access-us-financial
- https://www.fca.org.uk/news/press-releases/natwest-fined-264.8million-anti-money-laundering-failures#:~:text=NatWest%20fined%20%C2%A3264.8%20million%20for%20anti%2Dmoney%20laundering%20failures%20%7C%20FCA
- https://membercheck.com/blog/top-aml-ctf-penalties-in-2023/#:~:text=Binance%20fined%20%244%20Billion%20for,faces%20a%20%24186%20Million%20Fine

Subscribe
To keep yourself updated on the latest technology and industry trends subscribe to the Infosys Knowledge Institute's publications
Count me in!