Digital Supply Chain
Empowering Green Healthcare: Oracle JD Edwards' Sustainability Revolution
The healthcare industry is grappling with significant challenges related to medical waste disposal and greenhouse gas emissions, which heavily impact our environment. To combat this, healthcare organizations are setting ambitious targets to reduce carbon footprints and conserve resources, promoting greener practices. The demand for reprocessed medical devices is on the rise, projected to hit $12 billion by 2030. A key focus is on reprocessing surgical and patient care equipment to enhance environmental friendliness. This paper delves into the critical role of medical sustainability solutions, highlighting reprocessing strategies within the healthcare sector using Oracle JD Edwards (JDE). It details complex business processes for the safe and efficient reuse of medical devices, alongside part movement within the supply chain.
Insights
- Lifecycle management of medical devices, from procurement to disposal, is centered on reverse logistics, which involves the collection, sorting, and reprocessing of returned items
- The reprocessing intelligence capabilities of Oracle JD Edwards are enhanced by leveraging AI and machine learning to automatically assess the condition of returned items and determine the appropriate reprocessing techniques
- This approach enables data-driven decision-making, minimizes waste, and maximizes resource utilization
Introduction
The sustainability process emphasizes reuse and recycle mindset. Medical equipment manufacturers foster a healthier supply chain with hospitals by creating a redistribution chain, allowing hospitals to purchase products at reduced prices directly from the manufacturers. These business processes are comprehensive and come with various system-related challenges.
As healthcare systems worldwide aim to optimize resource utilization and minimize environmental impact, medical device reprocessing becomes a crucial strategy. However, ongoing research is necessary to continuously improve reprocessing techniques, validate their effectiveness, and address emerging challenges to ensure patient safety remains a top priority in this sustainable healthcare practice.
Medical devices contribute to carbon emissions throughout their entire lifecycle, from raw material extraction and manufacturing to transportation, usage, and disposal. Given their significant carbon footprint, reprocessing these devices is an environmentally sustainable practice.
Industry research and AMDR (Association of Medical Device Reprocessors) reports shows statistics which highlight the economic and environmental benefits of Medical Device Reprocessing.
Figure 1. Benefits of Medical Device Reprocessing

Analyzing the Pharmaceutical Industry Carbon Footprint through various research papers shows substantial contribution from Biotechnology, Pharma/ Medical Sector.
- In terms of Indirect Emissions (Scope 3), pharmaceuticals and chemicals are the biggest contributors, accounting for 18% of the healthcare sector's total emissions.
- The healthcare sector is responsible for 4.4% of global carbon emissions, with approximately 71% of these emissions coming from the supply chain, including the production and transportation of pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- On average, healthcare carbon emissions account for 4.4% of national carbon emissions globally.
Various studies and research highlight the environmental benefits of reprocessing medical devices, including significant reductions in carbon emissions and waste.
- A study by Stryker Sustainability Solutions comparing the carbon footprint of reprocessed single-use medical devices found that reprocessing can reduce carbon emissions by up to 50%.
- Medline ReNewal, in collaboration with Northwestern's Master of Science in Energy and Sustainability program, found that reprocessing a tissue sealing device resulted in a 40% reduction in carbon emissions compared to its single-use counterpart.
Reprocessing Business Case
The medical device reprocessing business process is a complex system with multiple key stages to ensure the safe and efficient reuse of medical devices. It involves close collaboration between device manufacturers, hospitals and clinics that use the devices for surgeries, and logistics and warehousing partners who manage the devices at various points in the supply chain.
End-to-End working model
The process usually starts with collecting single-use devices, which are then meticulously cleaned to remove any biological residues and contaminants. Next, the devices undergo thorough inspection, testing, and, if needed, repairs to meet specific quality standards. Once they pass these checks, the devices are sterilized to eliminate any remaining microorganisms, ensuring they are safe for reuse.
This systematic approach not only helps healthcare facilities save costs but also emphasizes the critical importance of upholding the highest standards of patient safety throughout the entire reprocessing lifecycle.
Figure 2. Reprocessing business flow in medical industry
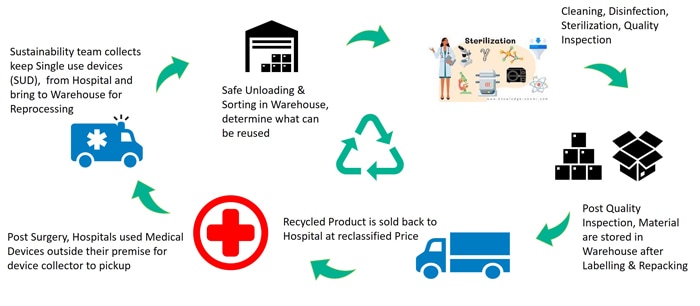
It is important to note that not every device on the market can be reprocessed in this model. However, it broadly applies to many single-use devices that are reusable. Many disposable devices are intended for use by a single patient and should not be reused for another. There are governance guidelines, such as those from the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), that specify which devices can be reprocessed. These guidelines require strict adherence to procedures ensuring patient safety and quality after reprocessing.
Reward Program and Customer Credit Cycles
To encourage customers to engage in sustainability practices and choose reprocessed medical devices, a reward system can be implemented. Establishing a loyalty program where customers earn points or discounts for sustainable actions, such as properly disposing of old devices for reprocessing or opting for reused medical equipment, can be effective. Additionally, offering exclusive benefits like priority access to new products or educational resources on sustainability can further motivate customer participation. Recognizing and publicly acknowledging customers who consistently make eco-friendly choices can also foster a sense of community and pride. By integrating rewards with sustainability efforts, businesses not only motivate customers to contribute to environmental well-being but also build a loyal customer base committed to ethical choices in healthcare procurement.
Customers, including hospitals and clinical care centers that purchase medical devices from the company, benefit from this program. The sustainability process not only promotes a greener environment but also provides rewards for the customer community participating in the program.
Figure 3. Customer Reward Flow

Solution challenges to address overall sustainability needs
Below are the typical challenges faced by mid-market Industry Clients, who have diverse applications for managing business processes, and have a lot of product lines.
- Multiple legacy applications are used at different stages of the sustainability process, and they are not well-integrated, leading to inefficiencies in system management.
- ERP functionalities are underutilized, limited to Inventory updates, Batch/Lot controls, and hold/releases.
- There is a lack of visibility of collected devices from hospitals due to the involvement of multiple systems, with many functions performed outside the system, making batch tracking extremely difficult.
- Adapting the software to track and manage sustainability metrics, such as carbon footprint or resource usage, may require significant customization and careful alignment with organizational goals.
- Sustainability involves creating an environment for hospitals to place demands, receive Make-to-Order products more quickly, and be rewarded for participating in reprocessing and receiving promotional benefits. There is no single system to track the entire process.
High Level Medical Sustainability Reprocessing Flow mapped to Oracle JD Edwards
Oracle JD Edwards EnterpriseOne can be leveraged to manage the entire End-to-End business process flow in Medical Device Reprocessing, thus rationalizing the application landscape. It offers comprehensive ability to Collect and Maintain various data sets, Model the various transaction flows, Predict and Plan the Flow chain, integrate well with other cloud-based systems, and be able to Report and generate various insights.
Below figure represents high level process flow using various modules of Oracle JD Edwards. The critical functionality triggers are,
- Lot/Serial Number, Lot Grade, and other Lot Control Attributes.
- Country of Origin activation.
- Cost Components, Routing Instructions.
- Supplemental Database – to track the detailed information about the sustainability attributes of the medical device, such as materials used, recyclability, and compliance with environmental standards.
- Media objects/Category Codes – to track the notes or information related to the environmental impact or special handling instructions for sustainable practices.
- Supplier Master – track Suppliers who meet sustainability criteria, ensuring that the medical devices sourced are from environmentally responsible vendors.
Figure 4. Oracle JDE Mapping for medical device reprocessing
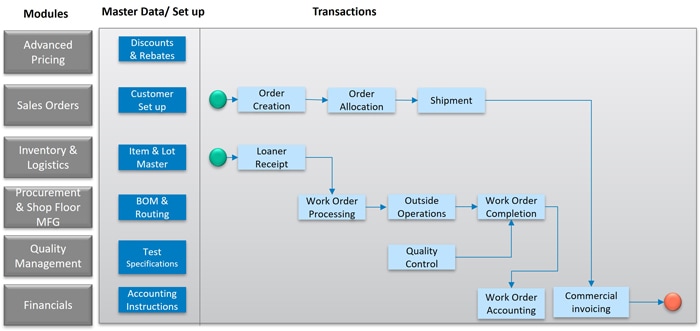
Modular functionalities in Oracle JD Edwards
- Device Collection & Unloading: Hospital used devices which are eligible for reprocessing are collected using labelled containers. Device collectors print the required number of labels to collect items.
- Receipt and Sorting: Containers arrive at the manufacturer's Receiving dock, the labels are carefully Opened, Segregated, and initial inspection is carried out. At this stage, some items can be rejected and trashed if they are damaged beyond repair.
- Reprocessing Work Orders: Work Orders are then opened for the item to enter in to Reprocess cycle. Routing steps will have Cleaning, Sterilization, Assembly, and Labelling operations.
Items will also go for outside operation where vendor partner will perform specialized processing/ Gamma sterilization etc.
Backflush Completion is then done to stock the Reprocessed item. The type of lot and numbering distinguish the Reprocessed items. Lots are put on hold till the quality team completes verification. - Quality Inspection: Test scenario templates are tailored for product categories and will show a detailed checklist of areas to be inspected with boundary parameters to validate. If the results are passed, then the quality hold is released.
- Packing and Stocking: Completion with Backflush is done to account for Labor and overhead efforts.
- Customer Reward Program: Forecast is initially created to determine the demand and accordingly the supply planning is carried out. A customer's performance is monitored to see how much of the goods returned by him meets good reprocessing criteria and as well as turnaround time of the customer. One View Reporting can generate the necessary assessment metrics.
Specialized Pricing/ Discounts are offered for those customers who reorder the product devices which can be allocated from the reprocessed lots.
Functionalities and Capabilities
It includes all the automations on business processes, with reporting, analytics, and assessment functionalities to meet the overall objectives of sustainability process.
Figure 5. JDE sustainability process functionalities

Business Benefits
- A single Oracle JD Edwards system tracking the entire business flow from forecasting to supply and reprocessing to stock.
- Batch tracking and visibility at every stage of processing.
- Automation to enhance efficiency.
- Faster supply chain and improved customer loyalty engagements.
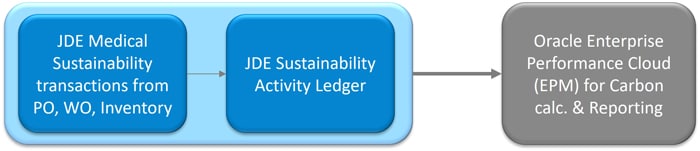
Integrate the solution with Standard Oracle JD Edwards Sustainability Framework
Oracle JD Edwards has recently enhanced its functionality by introducing the JDE Sustainability Framework, which can capture environmental data and record it in the Sustainability Activity Ledger. Transactions related to medical sustainability, recorded through various modules such as Inventory, Procurement, and Manufacturing, seamlessly integrate with the JDE Sustainability Framework. This data can then be fed into Carbon Calculation Software for comprehensive analytics and reporting. This integration provides a complete end-to-end process cycle, from facilitating medical sustainability transactions to recording them in the JDE Sustainability Framework.
AI and IoT based technology to digitize the Inventory Management and Device Tracking
The reprocessing of medical devices can be significantly improved by utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, which enhance efficiency and drive digitization, thereby improving the end-to-end supply chain. Here are some key areas of improvement:
- Demand Forecasting: AI algorithms can accurately predict future inventory requirements by analyzing historical data, market trends, and seasonal patterns.
- Robotic Quality Check: Automated quality inspection and validation of collected devices to determine if they can be reprocessed further.
- Reporting and Analytics: AI can enable real-time reporting and analyze vast amounts of data to uncover patterns and detect anomalies.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can assess incoming devices from hospitals to determine the level of maintenance required for them to operate as intended.
Tracking medical devices is crucial throughout the supply chain, especially considering their size and usage, to quickly address and resolve any issues. Efficient tracking mechanisms enable manufacturers to easily locate products when needed, thereby improving patient safety and reducing risks.
IoT and AI can enhance device tracking solutions by offering Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS), providing real-time visibility of medical devices and their status. From an inventory management perspective, manufacturers should implement serial number assignments, barcodes/QR codes, and RFID technologies in their products to facilitate detailed tracking and inventory control.
Other Specialized Cloud Apps in Market for Medical Device Tracking
There are several cloud-based medical device tracking systems available that can help healthcare facilities manage and monitor their medical devices efficiently. Here are a few notable ones:
- VueTrack: This system uses advanced barcode scanning and cloud-based technology to track, document, and manage medical devices and supplies from delivery to point of care. It offers real-time, accurate data and web-based reports.
- AiRISTA: AiRISTA provides a comprehensive medical device tracking and traceability system that enhances patient safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. It integrates advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain for optimized tracking.
- Timly Software System: Timly offers a single online platform for tracking medical devices, allowing users to manage and monitor assets, identify faulty devices, and keep track of medical supplies.
These systems can significantly improve inventory management, reduce waste, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Regulatory Standards associated with medical device sustainability
Regulatory standards for medical device sustainability focus on ensuring that devices are safe, effective, and environmentally friendly throughout their lifecycle. Here are some key standards and regulations:
- ISO 13485: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system, ensuring that an organization can consistently provide medical devices and related services that meet both customer and regulatory expectations.
- ISO 14971: This standard outlines the application of risk management to medical devices, ensuring that potential risks are identified, evaluated, and mitigated.
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive): This EU directive limits the use of certain hazardous materials in electrical and electronic products, including medical devices.
- WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive): This EU directive establishes collection, recycling, and recovery targets for all types of electrical goods, including medical devices.
- FDA Regulations: In the United States, the FDA enforces regulations that include environmental considerations, such as the use of safe materials and proper disposal methods.
Conclusion
Reprocessing medical devices contributes to a greener environment and enhances the sustainability of the medical and healthcare industries. The associated processes, safety, and compliance requirements are crucial and must be strictly followed to avoid adverse impacts on the healthcare ecosystem. This necessitates a meticulously designed process and comprehensive functionalities supported by an IT system. Infosys Oracle JD Edwards, in conjunction with Infosys Cobalt, offers an end-to-end solution for the sustainability process, ensuring an unbroken chain of operations with specialized capture, tracking, and processing functionalities.
References
- Understanding Medical Device Tracking and Traceability | AiRISTA Blog
- Factors Affecting Quality of Reprocessing | FDA
- Reprocessed Medical Devices Market Size Report, 2030
- Reprocessing-By-the-Numbers-2021-US-VERSION-GLOBAL-DATA-FINAL.pdf
- 2023 Carbon Impact of Biotech & Pharma Report
- Comparative Carbon Footprint for LCA.pdf

Subscribe
To keep yourself updated on the latest technology and industry trends subscribe to the Infosys Knowledge Institute's publications
Count me in!