Artificial Intelligence
Use Cases of Generative AI in Enterprise Architecture Practice
This whitepaper explores how the integration of Generative AI (GenAI) within the enterprise architecture domain presents transformative opportunities. By leveraging GenAI, organizations can enhance decision-making, optimize processes, and drive innovation. The use cases explored in this document demonstrate how GenAI can align technology with business objectives, improve efficiency, and support strategic goals. As enterprises continue to evolve, the adoption of GenAI will be pivotal in creating adaptive, scalable, and sustainable architectures that meet future demands. Embracing this technology will not only provide a competitive edge but also foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Insights
- This Point of View paper discuss on the Purpose of Enterprise Architecture in an IT Organization
- Role of GenAI in EA Operations and its Use Cases
- Important Risks & Considerations
- Leading EA tools & their AI capabilities
Introduction
Many of today's enterprises find themselves in a state of flux. On one side, their customers are accustomed to interacting with AI through various digital-native brands, which sets similar expectations for other brands. Employees also wish comparable engagement experiences from their employers.
Conversely, these enterprises are burdened with legacy systems and processes that hinder their progress towards modernization. Despite efforts to remain relevant, most enterprises are not adequately prepared to embrace emerging trends and stay ahead of the curve.
The crucial responsibility of preparing enterprises for this challenge lies with the Enterprise Architecture (EA) team. As EAs strategize to make the enterprise future-ready, a pertinent question arises: to what extent are EAs themselves using the full spectrum of technological advancements, such as the powerful Generative AI?
This article aims to share our perspective on how EAs can use Generative AI to support the development of a modern enterprise.
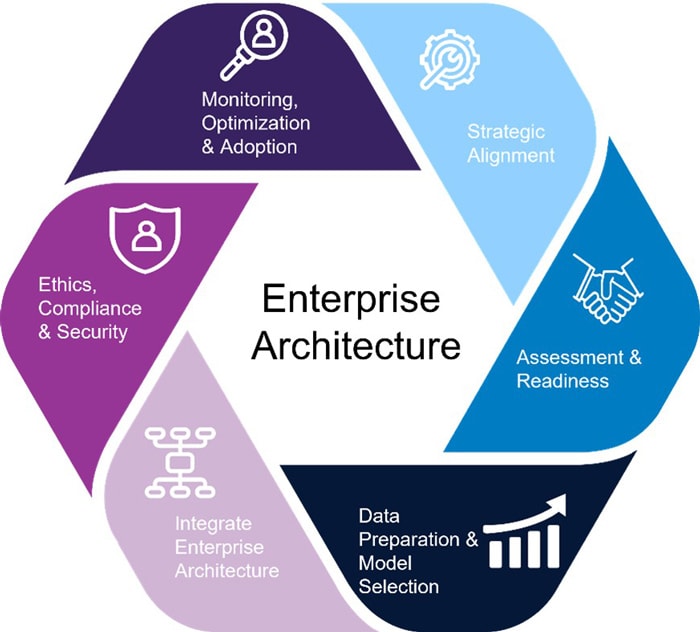
Purpose of Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise architecture serves as a cornerstone across various sectors, providing a systematic approach to harmonize technological advancements with organizational objectives. This alignment is essential for companies aiming to leverage technology to boost profitability, enhance service delivery, and reduce operational expenses. The methodology delivers a well-defined blueprint for creating and evaluating enterprise frameworks, covering key dimensions like business, data, application, and technology layers.
- Business Architecture: This dimension focuses on mapping out the connections among strategy, operational workflows, and business needs. It prioritizes customer experience aspirations, embedding a customer-centric perspective into the broader organizational plan. Acting as a guiding force within the enterprise framework, it ensures that each technological effort directly supports business success.
- Data Architecture: This segment centers on arranging and managing data throughout the organization. It promotes effective data handling that aligns with enterprise goals, enabling companies to extract valuable insights, strengthen decision-making capabilities, and meet their strategic targets.
- Application Architecture: Moving through the framework, this layer zeroes in on software development and integration. Its primary aim is to ensure that applications work smoothly alongside business operations. By designing efficient and purposeful software solutions, this layer enhances process performance and contributes to realizing long-term organizational ambitions.
- Technology Architecture: At the foundation, this layer addresses the infrastructure underpinning the applications. Its goal is to deploy technological solutions whether bespoke or off-the-shelf that meet present requirements while remaining flexible, scalable, and resilient enough to adapt to evolving future needs.
The following lists the key processes followed by the Enterprise Architecture function.
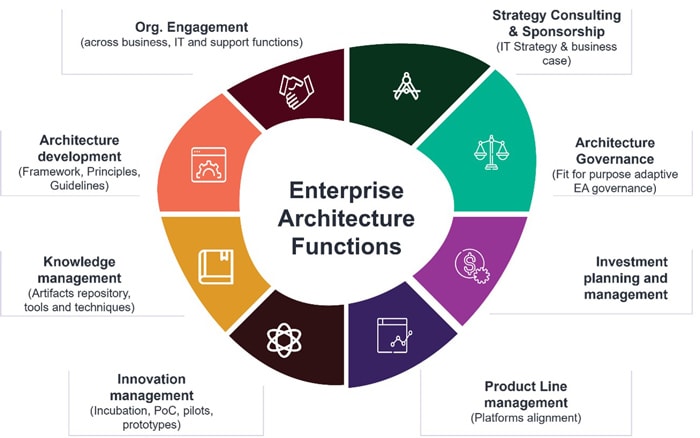
Enterprise architecture (EA) serves as a strategic tool to bridge the gap between an organization's ambitions and its current realities. Broadly, EA has two main objectives:
- Ensure seamless RUN operations.
- Adapt and drive CHANGE.
While specific teams execute projects aligned with these goals, EAs are primarily responsible for ideating, strategizing, and providing direction to predict issues and prepare for the future.
To ensure seamless RUN operations, EAs undertake the following actions:
- Prevent security breaches and service disruptions by consistently evaluating the technology landscape to identify and phase out outdated systems.
- Mitigate legal and regulatory risks by devising strategies to map data flows across the organization, track data lineage, and report data ownership.
- Reduce program implementation delays by accurately representing integration and dependencies.
- Prevent overspending through application rationalization and reducing redundancies.
For driving CHANGE, the EA team identifies proper use cases, retains, and recruits critical talent, advocates for change within the business, and designs the optimal technology stack required.
Foundational Elements of Enterprise Architecture:
Before exploring potential use cases for Generative AI in EA, let us examine the foundational activities performed by EAs:
- The primary activity is business capability mapping. By understanding the organization's goals, EAs evaluate the current state of applications and capabilities and map them to target state capabilities. For instance, a business selling fresh produce online might require an online ordering interface. If the enterprise's two-year roadmap includes facilitating multiple ordering modes, the EA must map out the missing capabilities needed to achieve that vision.
- The next step is to build an application inventory needed to deliver these business capabilities. Despite its clear simplicity, many businesses lack a centralized application inventory. With the rise of SaaS, many IT applications are purchased directly by the business without IT involvement, making it challenging to maintain an accurate list of applications.
- Having an application inventory is just the first step; it must be accurate, complete, and consistently maintained. Inventory data should include information such as supported business capabilities, managed processes, business owners, and involved users.
- This application inventory, along with the mapped business capabilities, forms the foundation for strategic initiatives such as application rationalization, portfolio assessment, and obsolescence risk management.
- Additionally, EAs participate in decision-making around software selection, talent planning, risk evaluation, and security assessment.
Role of Generative AI in EA operations
Generative AI (GenAI) stands out as a groundbreaking advancement in the realm of artificial intelligence, going beyond the capabilities of conventional machine learning systems. True to its name, GenAI excels at producing fresh content, spanning text, visuals, audio, and beyond. This ability to create makes it an invaluable asset for sectors that thrive on inventive solutions and forward-thinking approaches.
Moreover, GenAI cultivates a synergy between human ingenuity and computational power, opening doors to novel possibilities that were once out of reach. Grasping the trailblazing creative potential of GenAI is key to fully harnessing its transformative impact.
While AI is widely used for automation and decision-making, Generative AI excels in content generation and conversational interactions. Enterprise Architects (EAs) can receive help from integrating Generative AI in multiple areas. Given the nascent stage of GenAI, we believe the focus should be on expanding the breadth of its use cases rather than deepening its application in a single area. Some of the key Use Cases are listed below:
- Create Application Descriptions: During the creation of an application inventory, GenAI can automate the generation of relevant information, such as the application's purpose and the technology stack involved, especially when limited information is available.
- Chat Over “Anything”: Leveraging GenAI's conversational capabilities, EAs can access and interact with various artifacts, such as technical design documents, business requirements, data models, and technical blueprints. By integrating these into large language models (LLMs), EAs can ask questions and receive answers about these artifacts.
- Figure out Application Alternatives: When identifying alternatives for obsolete technologies, GenAI can suggest options based on parameters like functional fit, cost constraints, and relevance.
- Recommend Architecture Options: EAs often compare diverse options to select the one that aligns with organizational goals and constraints. By inputting these considerations into GenAI models, EAs can make quicker and more informed decisions.
- Automated Governance: Ensuring compliance with organizational and legal standards is a critical EA responsibility. GenAI can continuously check systems for security, data privacy, and protection, instantly flagging potential violations and vulnerabilities based on applicable legal standards.
- Transforming Business Strategy with Generative AI: Generative AI (GenAI) reshapes business strategies by revolutionizing customer engagement and driving creativity in product development. While traditional AI focuses on personalization, GenAI’s strength lies in its ability to sift through massive datasets, crafting highly individualized experiences that elevate the customer journey. Think personalized product suggestions, custom-curated content feeds, or virtual shopping companions. Its sophisticated language capabilities bring a warm, human-like feel to interactions, making it a vital asset for redefining customer connections. On the innovation front, GenAI sparks fresh ideas for product design, refining concepts through data analysis and iterative improvements. This hastens the prototyping phase, smoothing the path from initial sketches to functional models while sharpening usability feedback. By centering user needs, GenAI fosters a dynamic, inclusive design process that evolves continuously from start to finish.
- Enhancing Data Architecture through GenAI: GenAI redefines data architecture by boosting efficiency in data modeling, master data management (MDM), and visual representation. Drawing from vast pre-trained datasets, it quickly builds tailored data structures for specific business scenarios, speeding up processes and aligning seamlessly with company objectives. In MDM, GenAI automates the crafting of core data frameworks and proposes ways to uphold exceptional data integrity—covering precision, fullness, and coherence. This simplifies the task of managing and retrieving vital data, ensuring a clear, dependable picture of critical business components. On the security front, GenAI fortifies protections with cutting-edge encryption, shielding sensitive information from threats. For visualization, it delivers real-time, adaptable graphic insights, molding itself to different data types and tweaking display styles for maximum effectiveness.
- Revolutionizing Application Architecture with GenAI: GenAI transforms application architecture by offering pre-designed tools and building blocks, paving the way for robust app creation while letting architects focus on big-picture priorities. This streamlines workflows and keeps solutions in sync with practical needs. It also enhances API integration by recommending strategies tied to business goals, securing data exchanges, generating test scenarios, and enabling nimble API crafting. Plus, GenAI churns out thorough, current API documentation, ensuring everything stays fresh and user-friendly.
- Advancing Technology Architecture with GenAI: GenAI elevates technology architecture by steering the choice of cutting-edge solutions through detailed assessments of factors like flexibility, robustness, and future-readiness. It delivers bespoke recommendations that match business needs, evolving alongside changing tech landscapes and organizational demands to keep suggestions sharp. GenAI also turbocharges custom development by whipping up pristine code fragments, producing flawless functions and classes in any programming language. This slashes manual work, ramps up productivity, and aligns with coding norms for clarity, upkeep, collaboration, and uniformity.
At this point, the applications of GenAI have primarily impacted the periphery of the EA function. EAs can utilize GenAI as an assistant to handle routine tasks and offer augmented intelligence for less complex activities.
With improvements in accuracy, a broader range of use cases, and enhanced security and privacy measures, GenAI has the potential to significantly expand its impact on the EA function.
Some additional complex use cases of Generative AI in EA function (The Beginning of Endless possibilities):
| Strategic Consultancy & Sponsorship |
|
|---|---|
| Architecture Governance |
|
| Investment Planning and Managment |
|
| Product Line Managment |
|
| Innovation Management |
|
| Knowledge Management |
|
| Architecture Development |
|
| Organisation wide Engagement |
|
Risks & Considerations
Generative AI (GenAI) brings impressive benefits to the table, yet it also introduces notable hurdles that can’t be ignored. A pressing issue is sustainability, which has risen to prominence as a vital factor in tech adoption. Many organizations now prioritize sustainability within their technology architecture guidelines, using it as a benchmark when choosing solutions to upgrade their IT ecosystems.
For all its transformative power and creativity, GenAI comes with significant environmental drawbacks. The process of training its expansive models demands enormous computational resources, guzzling energy and releasing substantial carbon emissions that amplify ecological concerns. To counter this, efforts must focus on crafting algorithms that use less energy or pushing data centers toward renewable energy options, thereby shrinking GenAI’s environmental footprint.
Beyond that, GenAI stirs up challenges in managing change. Workers used to conventional approaches might struggle to adjust, calling for tailored training and upskilling initiatives to ease their transition into using GenAI effectively. Blending it with legacy systems could also demand rethinking organizational structures, along with redefining roles and duties. As a result, embracing GenAI requires a thoughtful strategy that plays to its strengths enhancing decision-making and streamlining everyday tasks while navigating these complexities.
| Cybersecurity |
|
|---|---|
| Copyright issues (Intellectual property theft) |
|
| Deepfakes |
|
| Hallucinations |
|
| Explainability & Reliability |
|
| Erosion of Human Thinking |
|
| Organizational impact |
|
Suggested measures:
| Measures | Impacts |
|---|---|
| Data Minimization | Enterprises should only collect and store personal data that is necessary for the generative AI system to function. This can reduce the amount of sensitive information that is vulnerable to breaches or unauthorized access. |
| Encryption | Sensitive personal data should be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access. Encryption can make it more difficult for attackers to read or manipulate data, even if they gain access to it. |
| Access Controls | Access controls are essential for restricting access to sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized individuals can view or modify it. These controls should operate on a "need to know" basis and undergo regular audits to maintain their effectiveness. |
| Monitoring | Enterprises should implement monitoring systems to detect and respond to security incidents. Monitoring systems can detect unusual activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration, and trigger alerts or automatic responses. |
| Privacy Impact Assessments (PIA) | Enterprises should perform Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) to pinpoint and mitigate privacy risks in generative AI systems. PIAs assist enterprises in comprehending the risks tied to the collection, storage, and utilization of personal data, and in identifying suitable measures to address these risks. |
| Transparency | Generative AI systems need to be clear about the methods of collecting, using, and sharing personal data. Users should be made aware of the reasons for data collection, the specific types of data being gathered, and the entities that have access to this information. |
| Data Protection Regulations | Generative AI systems should comply with applicable data protection regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA. Compliance with these regulations can help enterprises avoid legal or financial penalties and maintain the trust of their customers. |
| Ethical Considerations | Generative AI systems should be designed and deployed with ethical considerations in mind. Enterprises should consider the potential impact of generative AI on individuals and society, and take steps to avoid biases, discrimination, or other negative consequences. |
List of leading EA Tools and their AI Capabilities
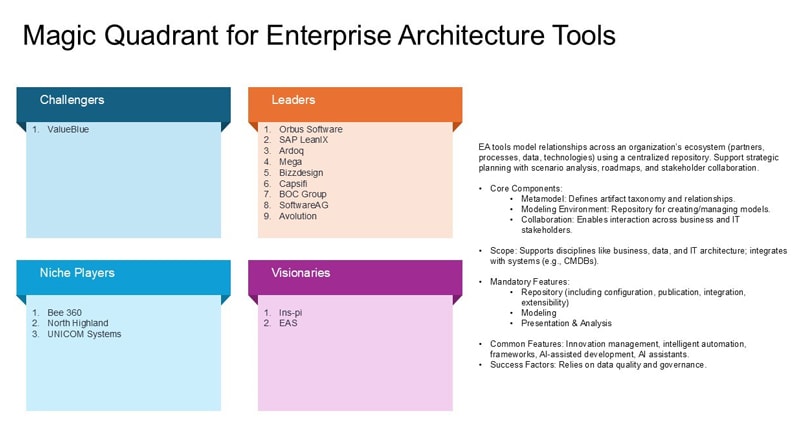
- SAP LeanIX: SAP LeanIX EAM is a SaaS solution hosted on Azure. It operates directly in North America, EMEA, APAC, and LATAM, with a significant customer base in manufacturing, finance, and retail sectors. The future roadmap includes features like an AI inventory builder, architecture recommendations, and executive dashboards with KPIs. SAP finalized its acquisition of LeanIX in November 2023. SAP LeanIX integrates various GenAI assistants and capabilities, such as OpenAI, SAP Business AI Copilot, and SAP AI Launchpad, to assist users in navigating reports and diagrams, and accessing product documentation guidance. Users can also utilize embedded AI to generate fact sheet descriptions, field names, and interrogate fact sheets. Additionally, SAP LeanIX offers efficient SaaS discovery features to quickly identify SaaS applications, assign them a confidence score, and automatically link them to application fact sheets, aiding in mapping the current IT landscape.
- Orbus Infinity: Orbus Infinity is a cloud-native, multitenant SaaS solution hosted on Microsoft Azure. Orbus Software mainly operates in the EMEA region, with an evenly distributed customer base between EMEA and North America. The company has a moderate presence in the APAC region and a minimal presence in LATAM. Orbus Software serves clients in the finance, government, manufacturing, and energy sectors. Future plans for Orbus Infinity include introducing a conversational UI (native CoPilot offering) as a service, a digital twin solution, and obtaining Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) authorization.
- Bizzdesign Horizzon: Bizzdesign's Horizzon, is available as SaaS solution, on-premises, or in a hybrid setup. It operates mostly in Europe and North America, now looking to expand in the Asia/Pacific region. Bizzdesign caters to various industries. Future developments for Horizzon include free-form diagramming, real-time collaborative web modeling, and AI-driven dynamic analytics.
In September 2024, Bizzdesign announced its merger with MEGA International. Both companies met the inclusion criteria for this MQ individually and were evaluated separately.
Bizzdesign has introduced several new AI features, such as a diagram importer/describer/styler/generator, a natural language analyzer, and dynamic analytics. Additionally, Bizzdesign has launched its AI-enabled "How-to Coach," a natural language chatbot that provides guidance on using and configuring Horizzon, based on product documentation and its knowledge base. - MEGA HOPEX: MEGA International's customer base and operations are widely distributed, with a significant concentration of resources in EMEA. The company serves clients in diversified sectors. Near term plans include AI-based data analysis, an AI-driven viewer portal, and enhanced architecture discovery.
HOPEX offers an AI classification service that automatically cleanses raw data imported from external repositories and features HEXA, a GenAI assistant powered by Azure’s OpenAI GPT, enabling users to inquire about HOPEX architecture using natural language. - Sparx Systems (Enterprise Architect): This versatile modeling tool supports UML, BPMN, and various other standards. It offers extensive modeling capabilities and is compatible with multiple enterprise architecture frameworks. However, it does not include any AI capabilities.
- Ardoq: Ardoq is a cloud-native SaaS solution, primarily operating in Europe and growing in North America. It serves clients in the financial services, public sector, and manufacturing industries. Plans for Ardoq include federated architecture access control, analytics across multiple solutions to support investment decisions, AI-based extraction of model items from unstructured information, and integrating lightweight process modeling capabilities into the tool.
During the research period for this MQ, Ardoq acquired ShiftX in September 2024, but this acquisition was not included in the evaluation. Additionally, Ardoq and Celonis announced a joint solution launch in September 2024, which was also not part of the evaluation.
Ardoq does not currently offer significant AI capabilities. - Abacus by Avolution: ABACUS is available as a hybrid cloud offering. It serves customers across various industries. Its operations span EMEA, North America, Latin America, and the Asia/Pacific region. Future enhancements for ABACUS include AI-driven recommendations to speed up diagramming, an administrator dashboard with improved analytics, traceability, and insights, and efficient information management across federated architectures.
The integration with Microsoft Copilot and the implementation of no-code algorithms enable both business professionals and nontechnical individuals to quickly create analytics for a variety of architectural questions. Furthermore, machine learning (ML) features improve the repository data's thoroughness, uniformity, and accuracy, providing insights and identifying data irregularities that might require review.
Comprehensive comparison of EA Tools & their AI/GenAI capabilities:
| AI Capabilities | Orbus Infinity | SAP LeanIX | Bizzdesign Horizzon | MEGA HOPEX | Sparx Systems | Ardoq | Abacus by Avolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creation or Modification of Application Descriptions | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Chat over "Anything" - RAG & Chatbot capabilities | P | No | P | P | No | No | P |
| Determine application alternatives | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Recommend Architecture options | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Automated Governance | P | Yes | P | P | No | No | P |
| GenAI In Shaping Business Strategy | P | No | P | P | No | No | P |
| Leveraging GenAI in Data Architecture | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| GenAI Integration in Application Architecture | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| GenAI’s Strengths for Technology Architecture | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
*P: Partial
Conclusion
The integration of Generative AI (GenAI) within the enterprise architecture domain presents transformative opportunities. By leveraging GenAI, organizations can enhance decision-making, optimize processes, and drive innovation. The use cases explored in this document demonstrate how GenAI can align technology with business objectives, improve efficiency, and support strategic goals. As enterprises continue to evolve, the adoption of GenAI will be pivotal in creating adaptive, scalable, and sustainable architectures that meet future demands. Embracing this technology will not only provide a competitive edge but also foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
References
During the development of this whitepaper, data and perspectives were gathered from various credible sources, such as research studies, articles, and other materials. Among the primary references that shaped the content of this whitepaper are:
These sources served as the basis for the discussions, insights, and suggestions presented within this whitepaper.

Subscribe
To keep yourself updated on the latest technology and industry trends subscribe to the Infosys Knowledge Institute's publications
Count me in!