Cloud
Harnessing the Power of Hybrid Cloud: Balance between Innovation and Risks in Financial Services
This whitepaper serves as a valuable reference for financial services enterprises navigating their cloud migration journeys. It emphasizes strategies for approaching innovation, some real-world use cases, process, and technology ideas while balancing the risks associated with hybrid cloud models, which is crucial in today's data-driven landscape.
Insights
- Financial services enterprises are prioritizing cloud transformation and modernization to leverage advanced platforms and technologies, focusing on modernizing workloads, migrating products, improving processes, and offering new services.
- Discusses common deployment models, including on-premises, public cloud, and private cloud, and highlights the risks and regulatory challenges that can hinder innovation.
- To balance innovation with risks, compliance and regulations, many enterprises are adopting hybrid deployment models. This paper will explore how the hybrid model addresses the challenges faced during cloud migration.
- Additionally, this paper serves as a comprehensive guide for financial services enterprises, providing strategies for innovation, real-world use cases, and key considerations for successfully deploying a hybrid cloud model in today's data-driven landscape.
Introduction
Hybrid cloud computing is transforming the financial services sector by combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources. This model helps enterprises balance innovation with compliance, addressing risks and regulatory challenges.
Financial services enterprises are prioritizing cloud transformation to modernize workloads, migrate products, improve processes, and offer new services. Common deployment models include on-premises, public cloud, and private cloud. Adopting a hybrid deployment model helps balance innovation with compliance, leveraging recent advancements in hybrid cloud technology to revolutionize IT infrastructure.
Financial services workloads range from legacy mainframe systems to cloud-native applications. Cloud transformation offers opportunities for performance, scalability, and cost optimization, despite challenges like data security, regulatory compliance, and vendor lock-in.
The hybrid cloud model has proven to be a strategic enabler for financial institutions, offering the perfect balance between innovation and security. Its ability to combine the best aspects of public and private clouds while maintaining regulatory compliance makes it an ideal choice for financial services organizations looking to drive digital transformation while ensuring data protection and operational efficiency.
Let us delve into a comprehensive technical representation of hybrid cloud models, covering both business and technical aspects, specifically tailored for business stakeholders, enterprise, and solution architects as well as cloud enthusiastic.
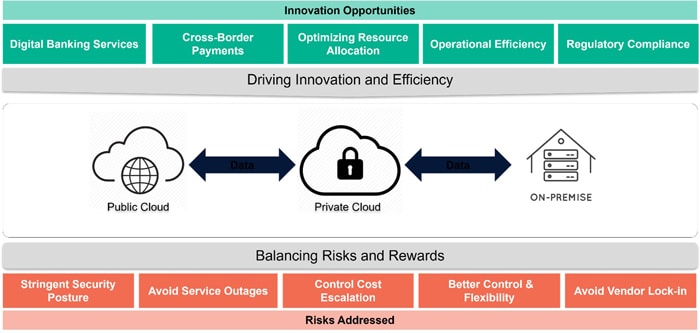
Figure 1: Hybrid Cloud Model – Opportunities and Challenging Zones
“A hybrid cloud banking environment gives banks the ability to run legacy workloads and sensitive data in a private cloud or on-premises data center, while also taking advantage of innovative services, scalable infrastructure, and new technologies offered by the public cloud.” - Source: Wikipedia
The Road to Cloud: Addressing Risk Management with a Hybrid Cloud Model
The cloud transformation of legacy systems and their integrated applications requires a thorough assessment and understanding to consider migration to the cloud. Traditionally, these systems are large and complex, capable of handling massive data, regulatory reporting, and maintaining a robust security posture. Additionally, they often involve vendor products or commercial off-the-shelf solutions that grapple with a multitude of constraints, which can impede their migration to the cloud and the adoption of advanced technologies.
Figure 2: General Risks and Mitigations
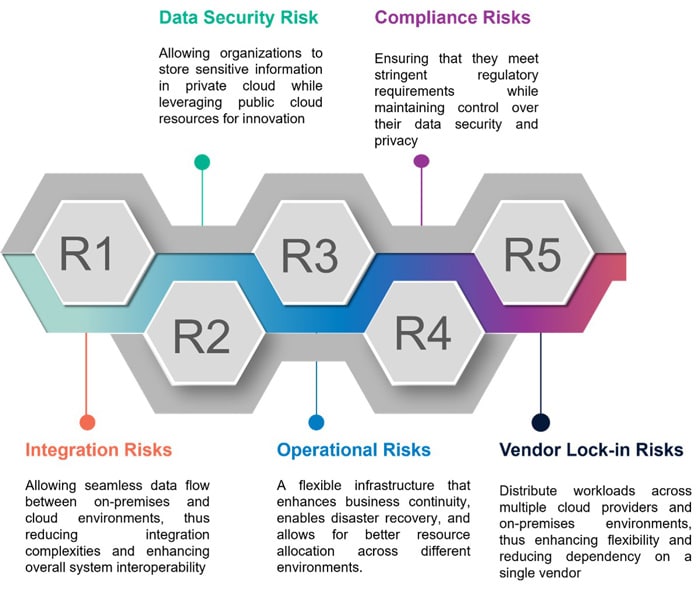
Along with these challenges and limitations, migrating regular workloads to the cloud is easy and manageable. However, the constraints surrounding critical risk dimensions necessitate the adoption of a hybrid model to leverage advanced technologies and foster innovation.
This section delves into the challenges and limitations inherent to cloud transformation programs and they can address through a hybrid cloud model.
Stringent Security Posture
The workloads deployed on public cloud and on-premises preview under network, data, applications security, and privacy. There is no doubt that each cloud deployment model has its own strengths and weaknesses in security. Notably, financial service enterprises have stringent requirements to protect customers and their data at various stages of product and service delivery.
Specific challenge: Fraud Detection and Prevention: Financial institutions must analyze large volumes of transaction data in real-time to identify and thwart fraudulent activities. This necessitates strong security protocols to safeguard sensitive customer information and adhere to strict regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
Avoid Service Outages
The workloads (core business) are subjective to keep up time and uninterrupted is the norm. A slight change in availability is vulnerable to the business model and market / customer expectations. Keeping key workloads on clouds is getting harder and challenging due to recent incidents on public clouds. Additionally, regulations are getting tightened to protect consumers and country interests.
Specific challenge: High-Frequency Trading (HFT) High-frequency trading firms require ultra-low latency and high availability to execute trades within microseconds. Service outages can lead to significant financial losses and missed trading opportunities. Ensuring continuous uptime and rapid recovery from any disruptions is critical.
Control Cost Escalation
Many enterprises operate with a mix of legacy systems and modern applications, leading to complexities in data synchronization, communication, and functionality. This integration complexity often results in operational inefficiencies, increased costs, and a slower response to market changes when the enterprise has independently operated two different deployment models.
Specific challenge: In a bank's legacy environment and technology landscape, the systems are built with a combination of COTS (Commercial Off-The-Shelf software) and applications that have spread across multiple hooks and interfaces. This has resulted in increased system dependencies, various data constraints, and complex correlations. The setup has introduced challenges in linking to the public cloud due to vulnerabilities surrounding security, technology limitations, and the costs associated with data transfer in and out of the cloud.
Better Control & Flexibility
Public cloud platforms designed to deliver services and products to multiple customers across the globe that force them to put major parts of infrastructure under control and connectivity. Some of these common limitations are slow down innovation and specific workloads requirements e.g., Unique hardware specifications for different financial datasets as per regulations.
Specific challenge: Financial institutions must comply with various regulatory requirements that dictate where and how data can be stored and processed. This often limits their control over data management and can complicate operations, especially when dealing with international transactions and data flows.
Avoid Vendor Lock-in
As enterprises increasingly adopt cloud solutions, the risk of vendor lock-in has emerged as a critical concern. Relying on a single cloud provider can limit an enterprise’s ability to adapt to changing business needs, technological advancements, or competitive pressures. In the financial services sector, where regulatory compliance and data security are paramount, avoiding vendor lock-in is essential for maintaining operational agility and ensuring data sovereignty.
Specific challenges: A large financial institution decided to migrate its core banking applications to a single cloud provider to take advantage of the cloud's scalability and cost-efficiency. Over time, the bank became heavily dependent on this provider for critical services, including data storage, transaction processing, and customer relationship management. As the bank's reliance on the cloud provider grew, cost escalated (data in & out), limited flexibility (unsupported technology), operation risks and compliance challenges (compliance gaps on the platform).
Balancing Act: Navigating Innovation and Risk with a Hybrid Cloud Model
The table offers a brief overview of innovation within the hybrid cloud framework. The Innovation Category identifies broad areas of focus, while the Innovation Opportunity highlights specific pursuits within those categories. The Associated Risks outlines potential challenges linked to these innovations, complemented by the Balancing Risks with Hybrid Cloud Model, which discusses strategies to mitigate these risks. Lastly, the Use Cases/Examples provides real-world applications, demonstrating how organizations successfully navigate the hybrid cloud landscape. Collectively, this summarization presents a holistic view of innovation opportunities based on wider knowledge and experience in hybrid cloud deployments.
Table 1: Innovations in Hybrid Cloud Deployment Model
| Innovation Areas | Innovation opportunity | Associated Risks | Risk Management | Use cases/Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Banking Services | Accelerated adoption of Open Banking while safeguarding Privacy | Data Security Risks: The potential for data breaches and unauthorized access, which can compromise sensitive information. Compliance Risks: The possibility of incurring significant penalties due to non-compliance with regulatory requirements. |
By implementing robust data storage and localization strategies, enhancing security controls, and providing a flexible architecture to ensure data privacy and protection. | Leading financial institutions in the US and UK regions have adopted hybrid cloud solutions to support their open banking initiatives while delivering innovative financial services. |
| Optimizing Resource Allocation | Technologies like Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) enhance communication between different cloud platforms, reducing latency and improving security. | Data Leakage: The risk of data leakage increases due to the interconnected nature of public and private clouds. SLA Mismanagement: Different SLAs between cloud providers can result in inconsistent service levels. |
Regularly encrypt data to protect it during transfer between public and private clouds and help to employ federated identity solutions and Zero Trust architectures to streamline authentication and enhance security. | Leading bank in USA, prefer to build critical workload cloud platform on private cloud and keep supporting workloads on public cloud. A major product which supports this design control and building flexible infrastructure on private cloud. Additional benefits are security, control, flexibility and avoid vendor lock-in. |
| Operational Efficiency | Offer significant innovation opportunities by combining the best of both public and private clouds and reducing costs and enhancing security of network, data, and applications. | Security Controls: Implement robust security controls based on risk treatment strategies, such as zero-trust models and encryption. Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor and optimize performance to address emerging risks and vulnerabilities. |
Due to complete control of space, regularly assessing risks, tolerance, and treatment strategies to identify critical assets and potential threats is easy to manage. Moreover, the model also helps to ensure compliance with governance frameworks by aligning policies across all cloud components. |
Largest and global bank of Canada has initiated cloud migration and modernization program where core systems would retain on private cloud and leveraging AWS cloud for supporting workloads. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Enhanced Data Protection and Cost Efficiency by leveraging private cloud for data protection and public cloud for data analytics. By keeping large datasets on private cloud reduces costs associated with in-out of public cloud infrastructure. | Data Sovereignty: Ensures data stored and processed in compliance with local regulations by using private clouds for sensitive data. Regulatory Changes: Provides flexibility to quickly adapt to new regulatory requirements without overhauling the entire IT infrastructure. |
Data under control helps by conducting frequent risk assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities if occurring in the private cloud and reduces attack surface for any threat. Developing comprehensive disaster recovery plans to maintain compliance and business continuity in case of disruptions that reduce hefty fine of regulations. |
Leading bank of UK explores the option to migrate legacy fraud detection and crime prevention systems under development by its SaaS replacement on private cloud. The SaaS product has different offerings and supports public cloud extension for additional features. |
Key Considerations for Financial Services Adopting a Hybrid Cloud Model
Adopting a hybrid cloud model offers financial services a balanced approach, combining the agility and cost-efficiency of public clouds with the security and control of private clouds. This enables enhanced operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and rapid innovation. However, careful consideration of data security, compliance requirements, and risk management is essential to successfully navigate the complexities of hybrid cloud deployment and fully realize its benefits. Here are the top 10 key considerations for financial services who are adopting hybrid cloud deployment model:
Table 2: Key Considerations
| Key Considerations | Use case description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Workloads | Hybrid cloud enables financial institutions to maintain critical infrastructure on premises while leveraging cloud scalability. |
| Regulation in action | Ensure compliance with evolving financial regulations by securely managing sensitive data across environments. |
| Technology advancement with control | Facilitate innovation with advanced technologies while retaining control over critical operations. |
| Multi-cloud infrastructure | Utilizes multiple cloud providers to enhance resilience and avoid vendor lock-in. |
| Data Pull and Push control | Provides seamless data transfer capabilities between private and public clouds for optimal performance and cost optimizations. |
| Business Oriented GenAI Capability | Leverages generative AI to enhance decision-making and customer experiences. |
| DC Exit Policy | Enables strategic exit from traditional data centers, reducing costs and improving agility. |
| SaaS infrastructure | Mitigates vendor lock-in risks by integrating SaaS solutions within a hybrid cloud framework. |
| Interoperability with Core Systems | Ensures seamless integration with legacy systems, enhancing operational efficiency. |
| Fencing Cybersecurity Threats | Strengthens defenses against cyber threats with robust security measures across hybrid environments |
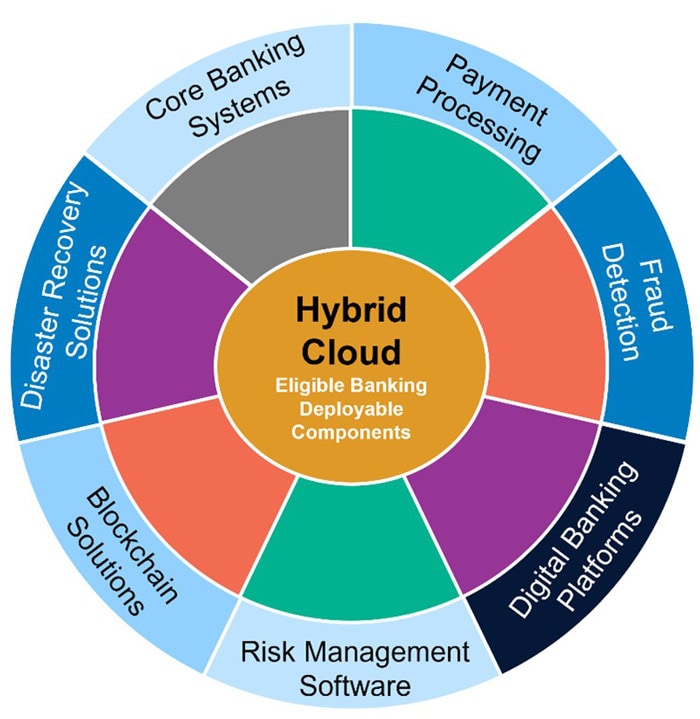
Hybrid cloud deployment in the banking sector enables the integration of various components to enhance operational efficiency and compliance. By leveraging both private and public clouds, banks can ensure robust security, real-time processing, and seamless interoperability with legacy systems. This approach allows financial institutions to meet stringent regulatory requirements, optimize costs, and innovate rapidly while maintaining control over sensitive data. Below the figure shows 7 deployable components where maximum innovative use cases are / will be developed and tested and integrated with a public cloud to serve wider customers to enhance their experiences.
Figure 3: Hybrid Cloud - Eligible Banking Deployable Components
Conclusion
In conclusion, adopting a hybrid cloud model is essential for financial services to navigate the complexities of modern regulatory requirements and operational challenges. By leveraging both public and private clouds, institutions can enhance their security posture, ensure continuous uptime, and manage costs effectively. This approach addresses specific challenges such as fraud detection, high-frequency trading, and avoiding vendor lock-in, while providing better control and flexibility over data management. Hybrid cloud deployment enables financial services to innovate securely, comply with stringent regulations, and maintain operational agility in a rapidly evolving market. This model accelerates transformation by providing testbeds for innovative products and services to build private clouds and scale it in public cloud infrastructure as needed.

Subscribe
To keep yourself updated on the latest technology and industry trends subscribe to the Infosys Knowledge Institute's publications
Count me in!