Digital Supply Chain
Transforming Medical Devices Manufacturing Processes using Robotics Integration with Oracle JD Edwards
This Medical Robotics refers to usage of Robotic systems in various medical devices, and this paper details various use cases and design involved in leveraging Oracle JD Edwards EnterpriseOne application for Medical Robotics functionality. It brings huge benefits to the medical industry by enhancing precision, increasing efficiency on various stages of business process.
This white paper provides readers with insights into the type of integration adopted and how technical architecture is involved between the Robots and Oracle JD Edwards EnterpriseOne (JDE) system. This model achieves continuous improvement by using Agentic AI in this integration.
Insights
- Procure to Pay Cycle – Robots can perform Devise Inspection post GRN Receipt, and subsequent Quality checks on Received Stock and determine if it meets standards. The feedback is integrated with JD Edwards for Procurement process updates.
- Manufacturing Process – Robots can do precision manufacturing and 3D printing of delicate devises and can be integrated into JD Edwards for various Manufacturing execution steps.
Introduction
Robotics plays a crucial role in enhancing the precision, efficiency, and safety of medical device manufacturing. Robots can continuously operate without fatigue and hence are most useful for contract manufacturers. They work methodologically resulting in faster production cycles, and with their precision the scrap waste will be less. Robots are the best fit to participate in manufacturing, especially in high-risk working environment, radiation hazards etc.
This paper discusses Oracle JD Edwards integration of Agentic AI, which further integrate with controlling software of physical machinery Robot to perform the tasks.
Business Benefits
- Enhanced Precision and Accuracy: Robots operate with such high precision that they significantly reduce costs associated with manual labor. They can easily handle manufacturing tasks that require intricate skills. Industry metric highlights that Robotic systems can boost production efficiency by up to 30%, reducing cycle times and increasing throughput.
- Increased Quality: Robots consistently meet safety, regulatory, and quality standards, resulting in a lower risk of defects in robot-driven production. Industry metric highlights that robots can lead to a 70% reduction in errors compared to manual processes.
- Intelligence and Scalability: Robots can be programmed to perform various tasks, showcasing their high intelligence. They can scale up or down based on production demands. Industry metric highlights that companies can achieve up to 20% savings in operational costs by automating repetitive tasks with robots.
- Reduced Workplace Risk: Robots can replace humans in high-risk work environments, thereby reducing the likelihood of accidents or hazards for human workers.
Robots in Procure to Pay Inspection Cycle
Quality and inspection in the medical device industry are exhaustive and detailed processes to ensure products meet compliance standards. It begins with issuing a purchase order to the supplier for device delivery. Once the products arrive at the dock, the quality control team conducts thorough inspections to certify their compliance with quality standards.
Human inspection of medical device procurement is challenging due to the intricate and precise nature of these devices. Manual inspections are prone to human error, fatigue, and inconsistencies, which can lead to defects being overlooked. Additionally, the high volume of devices and the need for stringent regulatory compliance make it difficult for human inspectors to maintain the necessary level of accuracy and efficiency.
Robotic inspection, on the other hand, offers a solution to these challenges. Robots can perform detailed and repetitive inspections with micro-level precision, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the risk of defects. They can operate continuously without fatigue, maintaining high productivity and accuracy. Furthermore, robots equipped with advanced sensors and AI can detect even the smallest anomalies, ensuring that all devices meet the required safety and regulatory standards. This makes robotic inspection an essential component in the procurement process of medical devices, enhancing overall quality and reliability.
Medical industry requires inspection during Product receipt at warehouse, for e.g. Orthopedic Instruments like Humerus Nail, Rods, Spanners has specific dimensions and characteristics to be fitted into surgical kits, and hence quality inspection checks are detailed in nature, and is time consuming.
Below are common gaps arising in the medical devise manufacturing industry during product conformance to stock.
- Incorrect Product label
- Incorrect product packaging
- Laser marking issues (missed to mark, incorrect locations, wrong content)
- Lot/ Batch mix is not accurate
- Dimensions of the product are not correct
Robots perform medical device product inspections with exceptional precision and consistency. Equipped with advanced sensors and high-resolution cameras, they can detect even the smallest defects and anomalies. Robots use AI algorithms to analyze data in real-time, ensuring that each device meets stringent quality and regulatory standards. Additionally, robots can carry out non-destructive testing methods, like ultrasonic or X-ray inspections, to evaluate the internal structure of devices without causing any damage.
Some Medical device industry examples are below
1. Inspection of Incoming Sterile Packaging
Scenario: Receiving sterile surgical kits or devices (e.g., scalpels, catheters).
Robotic Action:
- Uses high-res vision and AI to inspect:
- Packaging integrity (no punctures or tears)
- Label legibility and expiration dates
- Seal correctness (using edge detection and heat signature)
AI Outcome:
- Cross-checks label information with PO data in JDE (e.g., lot number, UDI codes).
- Identify mismatches or anomalies
2. Visual Verification of Pharmaceutical Labels
Scenario: Receipt of vials, ampoules, or blister packs
Robotic Action:
- Robot scans barcode, then uses OCR + AI vision to read:
- Product name
- Batch/lot
- Expiry date
- Tamper-evident seals
AI Outcome:
- Validates against JDE data in real time.
- Uploads result with photo records to the lot traceability module in JDE.
3. Surface Cleanliness Inspection of Surgical Instruments
Scenario: Receiving reprocessed or outsourced surgical instruments.
Robotic Action:
- Vision system uses UV/IR inspection to detect surface residues or contamination.
- Verifies markings, etchings, and sterilization indicators.
AI Outcome:
- AI evaluates cleanliness score.
- Automatically accepts/rejects instruments and writes inspection results to JDE QA module.
Transforming medical device manufacturing through robotic integration with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne, leveraging the Agentic AI Vision framework, represents a significant advancement in the industry. Agentic AI utilizes advanced reasoning and iterative planning to autonomously address complex problems, enhancing the capabilities of AI agents by accessing diverse data through accelerated AI query engines. These engines process, store, and retrieve information to refine generative AI models, utilizing techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to intelligently source the right information from a broad array of data sources. The framework's core components—perception, reasoning, action, and learning—enable AI agents to gather and process data from sensors, databases, and digital interfaces, analyze this data to make informed decisions, execute tasks, and continuously improve through feedback.
Figure 1: Procurement business flow in medical industry with AI triggered Robotic Inspection
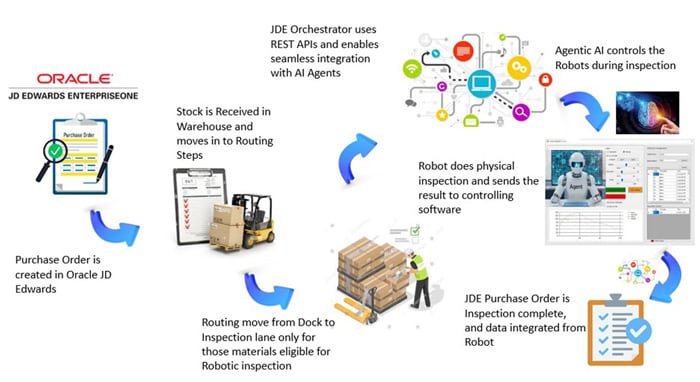
Figure shows how JD Edwards EnterpriseOne application trigger the Purchase Order and then it is integrated into Robotic software via middleware and the inspection result is updated back into JDE, thus Receiving the product to Stock. Oracle JD Edwards used Orchestrator to achieve this integration.
Advantage of using AI agent is that it is feedback oriented, it improves based on user interactions and learns from internet. This feedback helps to adjust the models and improve their accuracy.
Continuous Improvement loop with AI Agents
- AI agents continuously update their models based on new data and feedback. This is more useful for the medical industry, which requires larger compliance and control owing to patient safety.
- Techniques such as reinforcement learning enable agents to learn from their experiences.
- AI agents combine large language models (LLMs) with external tools to understand user queries, generate plans, and execute tasks. They process tool outputs, refine their approach, and iterate this process in a loop until achieving the desired result, ensuring efficient and dynamic problem-solving and marking a significant evolution in automation capabilities.
- AI Agents are trained in similar equipment or quality data. Raw/ Historical data is used to train the model. In this multi-agent framework different agents collaborate with each other for common goals. It can function in sequence where the first agent does a specific validation and pass on to next agent for subsequent validation, this cycle continues till the entire validation is complete.
Some examples in Procure to Pay inspection using AI Agentic Vision Framework
- Inspect with automatic parameters. It can analyze if there is repeated rejection from the same supplier and intensify the inspection
- It can analyze if there is a rollback on the selected lot and take decision on approval based on industry trends
- It can do supplier analysis and study the quality trend and take decisions
Figure 2: Procurement flow controlled by AI Agents
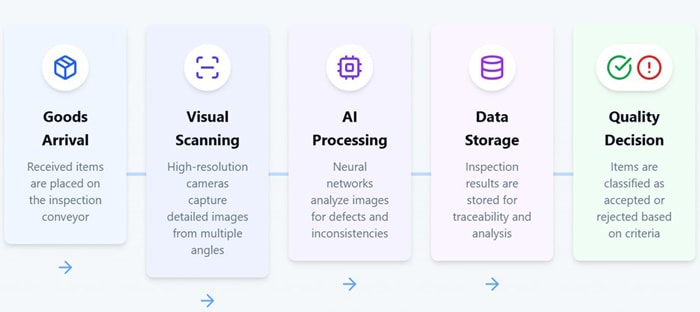
Controlling a physical robot for vision-based material inspection using an AI agent is a cutting-edge combo of robotics, computer vision, and artificial intelligence. Here's how this can be set up, step by step—from architecture to real-world flow.
Components Involved:
- AI Agent
- Central logic & decision-making unit
- Could be built using frameworks like OpenAI, TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Microsoft’s Azure AI
- Robotic Agent
- Computer Vision System
- Uses cameras (2D/3D, thermal, etc.) to capture material images
- AI models analyze defects, alignment, color, cracks, etc.
- Edge Device / On-Prem Server
- For real-time processing (especially where latency matters)
- Runs AI models, controls robot movements
- Central ERP - Oracle JD Edwards
- To log results, create quality reports, trigger rework orders
Workflow: AI Agent + Robot for Material Inspection
- Start Inspection
- Operator or system (e.g., JDE) sends a command to inspect a material batch.
- AI agent triggers the robot to start positioning via controller API.
- Robot Movement
- Robot arm moves to scan/photograph the material.
- Cameras capture high-res images.
- Image Analysis
- AI agent (using CV models like YOLOv8, Detectron, etc.) scans for:
- Scratches
- Misalignments
- Incorrect dimensions
- Surface defects
- AI agent (using CV models like YOLOv8, Detectron, etc.) scans for:
- Decision-Making
- If defects are detected, AI decides:
- Flag as reject
- Trigger another inspection
- Send data to JDE
- If defects are detected, AI decides:
- Action Trigger
- AI agent tells robot to mark/reject the item (e.g., move it aside, spray mark).
- It updates the JDE via API or message queue.
Technologies
| Component | Tools/Tech |
|---|---|
| AI Agent | OpenAI API, Oracle OCI AI Agentic Framework, LangChain, Azure AI, Python FastAPI |
| Robot Control | ROS, PLCs, Modbus, proprietary SDKs (e.g. FANUC) |
| CV Models | YOLO, OpenCV, TensorFlow, PyTorch, NVIDIA Isaac |
| Edge Processing | Jetson Nano/Orin, Intel NUC, Raspberry Pi |
| Integration Layer | REST API |
| ERP Logging | JD Edwards via Orchestrator APIs/ IOT |
Robots in Manufacturing Executions
Manufacturing transactions in ERP like Oracle JD Edwards EnterpriseOne trigger Production Work Order and is further processed into adding Bill of Materials and Routing instructions. Routing steps contain detailed manufacturing steps and if some steps involve Robots for advanced manufacturing, the order must be moved into specific work center where this work is carried out.
When integrated with JDE applications, robots receive work orders directly from the JDE application, which outlines the specific tasks and production schedules. As robots complete each task, they update the JDE application with real-time data on progress, inventory usage, and quality control metrics. This seamless integration ensures efficient workflow management, accurate tracking of production activities, and timely completion of work orders, ultimately enhancing overall productivity and product quality.
Oracle JD Edwards uses Orchestrator which in turn uses REST API to connect with control software of Robots. Once the manufacturing process is completed, JDE Orchestrations are trigged by Robots which will complete the Work Order in JDE.
Figure 3: Manufacturing business flow in the medical industry with AI triggered Robotic execution
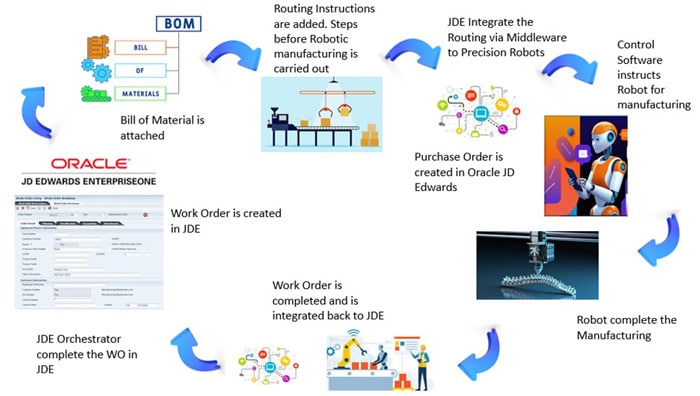
This AI uses Predictive Model, where it checks on what other similar equipment manufactured in prior years and passes similar instructions to the Robotic software. This has Real time checks, and Shop floor alert features.
- Train Models: Develop and train machine learning models using historical data to predict and optimize manufacturing processes. Improves quality using historical learning.
- Deploy Models: Deploy trained models to the AI software platform.
Robotic Control Integration
- Control Algorithms: Implement control algorithms in AI software to translate AI decisions into robotic actions.
- Communication Protocols: Establish communication protocols (e.g., MQTT, OPC-UA) for real-time data exchange between AI software and robots.
Conclusion
Integrating robotics with ERP systems in medical device manufacturing revolutionizes the industry by enhancing precision, efficiency, and quality, while also driving cost savings and improving compliance with regulatory standards. Robots bring unparalleled precision and consistency to the production process, ensuring high-quality outputs and reducing the risk of defects. By leveraging real-time data exchange, AI, and IoT technologies, robots can optimize production schedules, perform predictive maintenance, and streamline inventory management. This seamless integration not only boosts operational efficiency but also enhances decision-making and compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Ultimately, the synergy between robotics and ERP systems transforms medical device manufacturing, delivering superior products more efficiently and cost-effectively, and positioning companies for sustained competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market.
References

Subscribe
To keep yourself updated on the latest technology and industry trends subscribe to the Infosys Knowledge Institute's publications
Count me in!